mirror of
https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference.git
synced 2025-09-10 20:04:52 +00:00
commit
ed49379c6a
275
README-HF.md
Normal file
275
README-HF.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,275 @@
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Text Generation Inference
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub Repo stars" src="https://img.shields.io/github/stars/huggingface/text-generation-inference?style=social">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference/blob/main/LICENSE">
|
||||
<img alt="License" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/text-generation-inference">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.github.io/text-generation-inference">
|
||||
<img alt="Swagger API documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/API-Swagger-informational">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
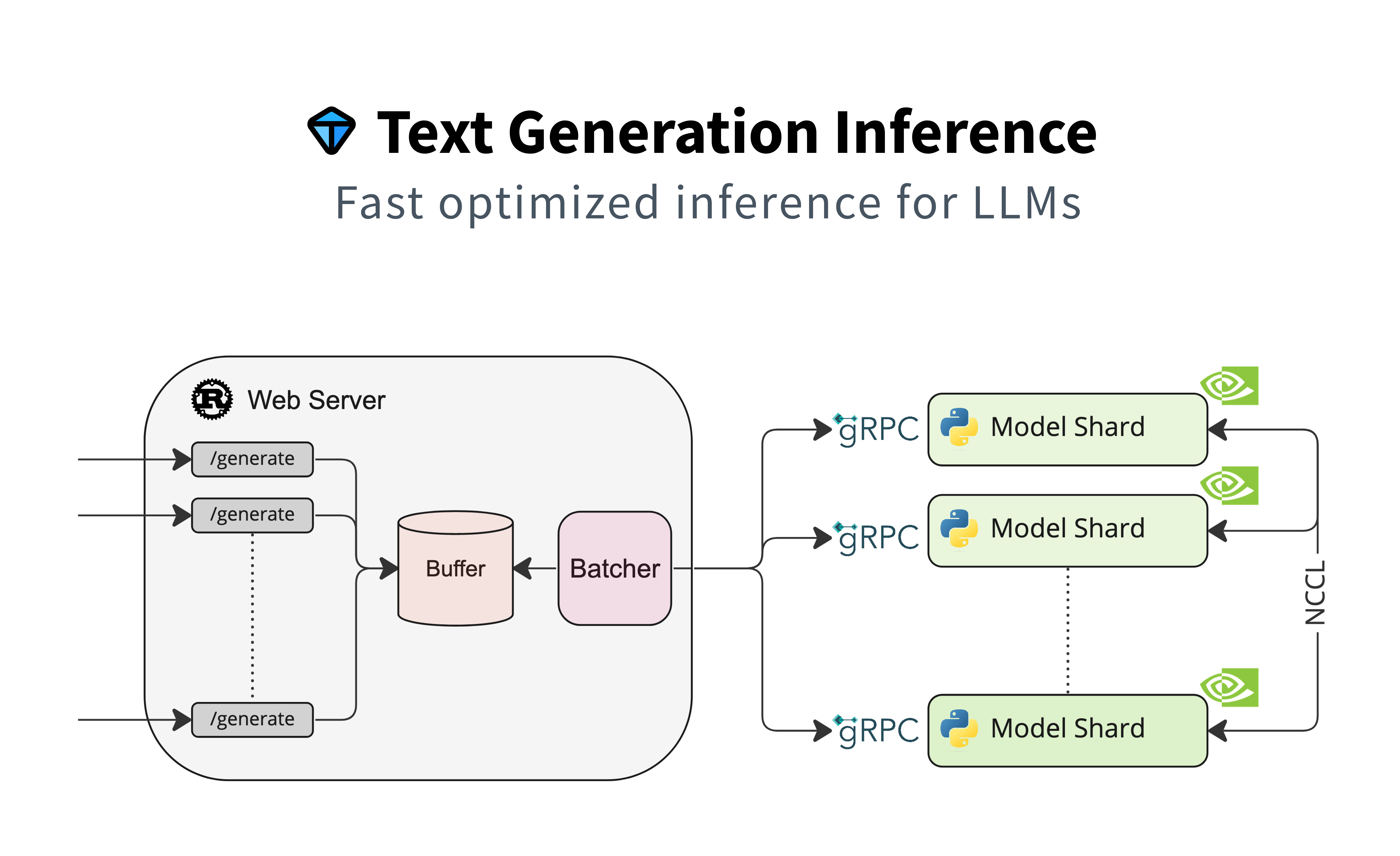
A Rust, Python and gRPC server for text generation inference. Used in production at [HuggingFace](https://huggingface.co)
|
||||
to power LLMs api-inference widgets.
|
||||
|
||||
## Table of contents
|
||||
|
||||
- [Features](#features)
|
||||
- [Optimized Architectures](#optimized-architectures)
|
||||
- [Get Started](#get-started)
|
||||
- [Docker](#docker)
|
||||
- [API Documentation](#api-documentation)
|
||||
- [Using a private or gated model](#using-a-private-or-gated-model)
|
||||
- [A note on Shared Memory](#a-note-on-shared-memory-shm)
|
||||
- [Distributed Tracing](#distributed-tracing)
|
||||
- [Local Install](#local-install)
|
||||
- [CUDA Kernels](#cuda-kernels)
|
||||
- [Run Falcon](#run-falcon)
|
||||
- [Run](#run)
|
||||
- [Quantization](#quantization)
|
||||
- [Develop](#develop)
|
||||
- [Testing](#testing)
|
||||
|
||||
## Features
|
||||
|
||||
- Serve the most popular Large Language Models with a simple launcher
|
||||
- Tensor Parallelism for faster inference on multiple GPUs
|
||||
- Token streaming using Server-Sent Events (SSE)
|
||||
- [Continuous batching of incoming requests](https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference/tree/main/router) for increased total throughput
|
||||
- Optimized transformers code for inference using [flash-attention](https://github.com/HazyResearch/flash-attention) and [Paged Attention](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm) on the most popular architectures
|
||||
- Quantization with [bitsandbytes](https://github.com/TimDettmers/bitsandbytes) and [GPT-Q](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.17323)
|
||||
- [Safetensors](https://github.com/huggingface/safetensors) weight loading
|
||||
- Watermarking with [A Watermark for Large Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.10226)
|
||||
- Logits warper (temperature scaling, top-p, top-k, repetition penalty, more details see [transformers.LogitsProcessor](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/internal/generation_utils#transformers.LogitsProcessor))
|
||||
- Stop sequences
|
||||
- Log probabilities
|
||||
- Production ready (distributed tracing with Open Telemetry, Prometheus metrics)
|
||||
|
||||
## Optimized architectures
|
||||
|
||||
- [BLOOM](https://huggingface.co/bigscience/bloom)
|
||||
- [FLAN-T5](https://huggingface.co/google/flan-t5-xxl)
|
||||
- [Galactica](https://huggingface.co/facebook/galactica-120b)
|
||||
- [GPT-Neox](https://huggingface.co/EleutherAI/gpt-neox-20b)
|
||||
- [Llama](https://github.com/facebookresearch/llama)
|
||||
- [OPT](https://huggingface.co/facebook/opt-66b)
|
||||
- [SantaCoder](https://huggingface.co/bigcode/santacoder)
|
||||
- [Starcoder](https://huggingface.co/bigcode/starcoder)
|
||||
- [Falcon 7B](https://huggingface.co/tiiuae/falcon-7b)
|
||||
- [Falcon 40B](https://huggingface.co/tiiuae/falcon-40b)
|
||||
- [MPT](https://huggingface.co/mosaicml/mpt-30b)
|
||||
- [Llama V2](https://huggingface.co/meta-llama)
|
||||
|
||||
Other architectures are supported on a best effort basis using:
|
||||
|
||||
`AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(<model>, device_map="auto")`
|
||||
|
||||
or
|
||||
|
||||
`AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(<model>, device_map="auto")`
|
||||
|
||||
## Get started
|
||||
|
||||
### Docker
|
||||
|
||||
The easiest way of getting started is using the official Docker container:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
model=tiiuae/falcon-7b-instruct
|
||||
volume=$PWD/data # share a volume with the Docker container to avoid downloading weights every run
|
||||
|
||||
docker run --gpus all --shm-size 1g -p 8080:80 -v $volume:/data ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:0.9.4 --model-id $model
|
||||
```
|
||||
**Note:** To use GPUs, you need to install the [NVIDIA Container Toolkit](https://docs.nvidia.com/datacenter/cloud-native/container-toolkit/install-guide.html). We also recommend using NVIDIA drivers with CUDA version 11.8 or higher.
|
||||
|
||||
To see all options to serve your models (in the [code](https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference/blob/main/launcher/src/main.rs) or in the cli:
|
||||
```
|
||||
text-generation-launcher --help
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can then query the model using either the `/generate` or `/generate_stream` routes:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl 127.0.0.1:8080/generate \
|
||||
-X POST \
|
||||
-d '{"inputs":"What is Deep Learning?","parameters":{"max_new_tokens":20}}' \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl 127.0.0.1:8080/generate_stream \
|
||||
-X POST \
|
||||
-d '{"inputs":"What is Deep Learning?","parameters":{"max_new_tokens":20}}' \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
or from Python:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
pip install text-generation
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from text_generation import Client
|
||||
|
||||
client = Client("http://127.0.0.1:8080")
|
||||
print(client.generate("What is Deep Learning?", max_new_tokens=20).generated_text)
|
||||
|
||||
text = ""
|
||||
for response in client.generate_stream("What is Deep Learning?", max_new_tokens=20):
|
||||
if not response.token.special:
|
||||
text += response.token.text
|
||||
print(text)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### API documentation
|
||||
|
||||
You can consult the OpenAPI documentation of the `text-generation-inference` REST API using the `/docs` route.
|
||||
The Swagger UI is also available at: [https://huggingface.github.io/text-generation-inference](https://huggingface.github.io/text-generation-inference).
|
||||
|
||||
### Using a private or gated model
|
||||
|
||||
You have the option to utilize the `HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN` environment variable for configuring the token employed by
|
||||
`text-generation-inference`. This allows you to gain access to protected resources.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if you want to serve the gated Llama V2 model variants:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Go to https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens
|
||||
2. Copy your cli READ token
|
||||
3. Export `HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN=<your cli READ token>`
|
||||
|
||||
or with Docker:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
model=meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf
|
||||
volume=$PWD/data # share a volume with the Docker container to avoid downloading weights every run
|
||||
token=<your cli READ token>
|
||||
|
||||
docker run --gpus all --shm-size 1g -e HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN=$token -p 8080:80 -v $volume:/data ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:0.9.3 --model-id $model
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### A note on Shared Memory (shm)
|
||||
|
||||
[`NCCL`](https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/nccl/user-guide/docs/index.html) is a communication framework used by
|
||||
`PyTorch` to do distributed training/inference. `text-generation-inference` make
|
||||
use of `NCCL` to enable Tensor Parallelism to dramatically speed up inference for large language models.
|
||||
|
||||
In order to share data between the different devices of a `NCCL` group, `NCCL` might fall back to using the host memory if
|
||||
peer-to-peer using NVLink or PCI is not possible.
|
||||
|
||||
To allow the container to use 1G of Shared Memory and support SHM sharing, we add `--shm-size 1g` on the above command.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are running `text-generation-inference` inside `Kubernetes`. You can also add Shared Memory to the container by
|
||||
creating a volume with:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
- name: shm
|
||||
emptyDir:
|
||||
medium: Memory
|
||||
sizeLimit: 1Gi
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and mounting it to `/dev/shm`.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, you can also disable SHM sharing by using the `NCCL_SHM_DISABLE=1` environment variable. However, note that
|
||||
this will impact performance.
|
||||
|
||||
### Distributed Tracing
|
||||
|
||||
`text-generation-inference` is instrumented with distributed tracing using OpenTelemetry. You can use this feature
|
||||
by setting the address to an OTLP collector with the `--otlp-endpoint` argument.
|
||||
|
||||
### Local install
|
||||
|
||||
You can also opt to install `text-generation-inference` locally.
|
||||
|
||||
First [install Rust](https://rustup.rs/) and create a Python virtual environment with at least
|
||||
Python 3.9, e.g. using `conda`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh
|
||||
|
||||
conda create -n text-generation-inference python=3.9
|
||||
conda activate text-generation-inference
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You may also need to install Protoc.
|
||||
|
||||
On Linux:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
PROTOC_ZIP=protoc-21.12-linux-x86_64.zip
|
||||
curl -OL https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf/releases/download/v21.12/$PROTOC_ZIP
|
||||
sudo unzip -o $PROTOC_ZIP -d /usr/local bin/protoc
|
||||
sudo unzip -o $PROTOC_ZIP -d /usr/local 'include/*'
|
||||
rm -f $PROTOC_ZIP
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
On MacOS, using Homebrew:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
brew install protobuf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then run:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
BUILD_EXTENSIONS=True make install # Install repository and HF/transformer fork with CUDA kernels
|
||||
make run-falcon-7b-instruct
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** on some machines, you may also need the OpenSSL libraries and gcc. On Linux machines, run:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
sudo apt-get install libssl-dev gcc -y
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### CUDA Kernels
|
||||
|
||||
The custom CUDA kernels are only tested on NVIDIA A100s. If you have any installation or runtime issues, you can remove
|
||||
the kernels by using the `DISABLE_CUSTOM_KERNELS=True` environment variable.
|
||||
|
||||
Be aware that the official Docker image has them enabled by default.
|
||||
|
||||
## Run Falcon
|
||||
|
||||
### Run
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
make run-falcon-7b-instruct
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Quantization
|
||||
|
||||
You can also quantize the weights with bitsandbytes to reduce the VRAM requirement:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
make run-falcon-7b-instruct-quantize
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Develop
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
make server-dev
|
||||
make router-dev
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Testing
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
# python
|
||||
make python-server-tests
|
||||
make python-client-tests
|
||||
# or both server and client tests
|
||||
make python-tests
|
||||
# rust cargo tests
|
||||
make rust-tests
|
||||
# integration tests
|
||||
make integration-tests
|
||||
```
|
||||
279
README.md
279
README.md
@ -1,208 +1,33 @@
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
# Text Generation Inference
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub Repo stars" src="https://img.shields.io/github/stars/huggingface/text-generation-inference?style=social">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference/blob/main/LICENSE">
|
||||
<img alt="License" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/text-generation-inference">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.github.io/text-generation-inference">
|
||||
<img alt="Swagger API documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/API-Swagger-informational">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
A Rust, Python and gRPC server for text generation inference. Used in production at [HuggingFace](https://huggingface.co)
|
||||
to power LLMs api-inference widgets.
|
||||
|
||||
## Table of contents
|
||||
|
||||
- [Features](#features)
|
||||
- [Optimized Architectures](#optimized-architectures)
|
||||
- [Get Started](#get-started)
|
||||
- [Docker](#docker)
|
||||
- [API Documentation](#api-documentation)
|
||||
- [Using a private or gated model](#using-a-private-or-gated-model)
|
||||
- [A note on Shared Memory](#a-note-on-shared-memory-shm)
|
||||
- [Distributed Tracing](#distributed-tracing)
|
||||
- [Local Install](#local-install)
|
||||
- [CUDA Kernels](#cuda-kernels)
|
||||
- [Run Falcon](#run-falcon)
|
||||
- [Run](#run)
|
||||
- [Quantization](#quantization)
|
||||
- [Develop](#develop)
|
||||
- [Testing](#testing)
|
||||
|
||||
## Features
|
||||
|
||||
- Serve the most popular Large Language Models with a simple launcher
|
||||
- Tensor Parallelism for faster inference on multiple GPUs
|
||||
- Token streaming using Server-Sent Events (SSE)
|
||||
- [Continuous batching of incoming requests](https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference/tree/main/router) for increased total throughput
|
||||
- Optimized transformers code for inference using [flash-attention](https://github.com/HazyResearch/flash-attention) and [Paged Attention](https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm) on the most popular architectures
|
||||
- Quantization with [bitsandbytes](https://github.com/TimDettmers/bitsandbytes) and [GPT-Q](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.17323)
|
||||
- [Safetensors](https://github.com/huggingface/safetensors) weight loading
|
||||
- Watermarking with [A Watermark for Large Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.10226)
|
||||
- Logits warper (temperature scaling, top-p, top-k, repetition penalty, more details see [transformers.LogitsProcessor](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/internal/generation_utils#transformers.LogitsProcessor))
|
||||
- Stop sequences
|
||||
- Log probabilities
|
||||
- Production ready (distributed tracing with Open Telemetry, Prometheus metrics)
|
||||
|
||||
## Optimized architectures
|
||||
|
||||
- [BLOOM](https://huggingface.co/bigscience/bloom)
|
||||
- [FLAN-T5](https://huggingface.co/google/flan-t5-xxl)
|
||||
- [Galactica](https://huggingface.co/facebook/galactica-120b)
|
||||
- [GPT-Neox](https://huggingface.co/EleutherAI/gpt-neox-20b)
|
||||
- [Llama](https://github.com/facebookresearch/llama)
|
||||
- [OPT](https://huggingface.co/facebook/opt-66b)
|
||||
- [SantaCoder](https://huggingface.co/bigcode/santacoder)
|
||||
- [Starcoder](https://huggingface.co/bigcode/starcoder)
|
||||
- [Falcon 7B](https://huggingface.co/tiiuae/falcon-7b)
|
||||
- [Falcon 40B](https://huggingface.co/tiiuae/falcon-40b)
|
||||
- [MPT](https://huggingface.co/mosaicml/mpt-30b)
|
||||
- [Llama V2](https://huggingface.co/meta-llama)
|
||||
|
||||
Other architectures are supported on a best effort basis using:
|
||||
|
||||
`AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(<model>, device_map="auto")`
|
||||
|
||||
or
|
||||
|
||||
`AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(<model>, device_map="auto")`
|
||||
|
||||
## Get started
|
||||
|
||||
### Docker
|
||||
|
||||
The easiest way of getting started is using the official Docker container:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
model=tiiuae/falcon-7b-instruct
|
||||
volume=$PWD/data # share a volume with the Docker container to avoid downloading weights every run
|
||||
|
||||
docker run --gpus all --shm-size 1g -p 8080:80 -v $volume:/data ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:0.9.4 --model-id $model
|
||||
```
|
||||
**Note:** To use GPUs, you need to install the [NVIDIA Container Toolkit](https://docs.nvidia.com/datacenter/cloud-native/container-toolkit/install-guide.html). We also recommend using NVIDIA drivers with CUDA version 11.8 or higher.
|
||||
|
||||
To see all options to serve your models (in the [code](https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference/blob/main/launcher/src/main.rs) or in the cli:
|
||||
```
|
||||
text-generation-launcher --help
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can then query the model using either the `/generate` or `/generate_stream` routes:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl 127.0.0.1:8080/generate \
|
||||
-X POST \
|
||||
-d '{"inputs":"What is Deep Learning?","parameters":{"max_new_tokens":20}}' \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
curl 127.0.0.1:8080/generate_stream \
|
||||
-X POST \
|
||||
-d '{"inputs":"What is Deep Learning?","parameters":{"max_new_tokens":20}}' \
|
||||
-H 'Content-Type: application/json'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
or from Python:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
pip install text-generation
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from text_generation import Client
|
||||
|
||||
client = Client("http://127.0.0.1:8080")
|
||||
print(client.generate("What is Deep Learning?", max_new_tokens=20).generated_text)
|
||||
|
||||
text = ""
|
||||
for response in client.generate_stream("What is Deep Learning?", max_new_tokens=20):
|
||||
if not response.token.special:
|
||||
text += response.token.text
|
||||
print(text)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### API documentation
|
||||
|
||||
You can consult the OpenAPI documentation of the `text-generation-inference` REST API using the `/docs` route.
|
||||
The Swagger UI is also available at: [https://huggingface.github.io/text-generation-inference](https://huggingface.github.io/text-generation-inference).
|
||||
|
||||
### Using a private or gated model
|
||||
|
||||
You have the option to utilize the `HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN` environment variable for configuring the token employed by
|
||||
`text-generation-inference`. This allows you to gain access to protected resources.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if you want to serve the gated Llama V2 model variants:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Go to https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens
|
||||
2. Copy your cli READ token
|
||||
3. Export `HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN=<your cli READ token>`
|
||||
|
||||
or with Docker:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
model=meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf
|
||||
volume=$PWD/data # share a volume with the Docker container to avoid downloading weights every run
|
||||
token=<your cli READ token>
|
||||
|
||||
docker run --gpus all --shm-size 1g -e HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN=$token -p 8080:80 -v $volume:/data ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:0.9.3 --model-id $model
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### A note on Shared Memory (shm)
|
||||
|
||||
[`NCCL`](https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/nccl/user-guide/docs/index.html) is a communication framework used by
|
||||
`PyTorch` to do distributed training/inference. `text-generation-inference` make
|
||||
use of `NCCL` to enable Tensor Parallelism to dramatically speed up inference for large language models.
|
||||
|
||||
In order to share data between the different devices of a `NCCL` group, `NCCL` might fall back to using the host memory if
|
||||
peer-to-peer using NVLink or PCI is not possible.
|
||||
|
||||
To allow the container to use 1G of Shared Memory and support SHM sharing, we add `--shm-size 1g` on the above command.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are running `text-generation-inference` inside `Kubernetes`. You can also add Shared Memory to the container by
|
||||
creating a volume with:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
- name: shm
|
||||
emptyDir:
|
||||
medium: Memory
|
||||
sizeLimit: 1Gi
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and mounting it to `/dev/shm`.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, you can also disable SHM sharing by using the `NCCL_SHM_DISABLE=1` environment variable. However, note that
|
||||
this will impact performance.
|
||||
|
||||
### Distributed Tracing
|
||||
|
||||
`text-generation-inference` is instrumented with distributed tracing using OpenTelemetry. You can use this feature
|
||||
by setting the address to an OTLP collector with the `--otlp-endpoint` argument.
|
||||
|
||||
### Local install
|
||||
|
||||
You can also opt to install `text-generation-inference` locally.
|
||||
|
||||
First [install Rust](https://rustup.rs/) and create a Python virtual environment with at least
|
||||
Python 3.9, e.g. using `conda`:
|
||||
First [install Rust](https://rustup.rs/):
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh
|
||||
|
||||
conda create -n text-generation-inference python=3.9
|
||||
conda activate text-generation-inference
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You may also need to install Protoc.
|
||||
Install conda:
|
||||
|
||||
On Linux:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl https://repo.anaconda.com/pkgs/misc/gpgkeys/anaconda.asc | gpg --dearmor > conda.gpg
|
||||
sudo install -o root -g root -m 644 conda.gpg /usr/share/keyrings/conda-archive-keyring.gpg
|
||||
gpg --keyring /usr/share/keyrings/conda-archive-keyring.gpg --no-default-keyring --fingerprint 34161F5BF5EB1D4BFBBB8F0A8AEB4F8B29D82806
|
||||
echo "deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/conda-archive-keyring.gpg] https://repo.anaconda.com/pkgs/misc/debrepo/conda stable main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/conda.list
|
||||
sudo apt update && sudo apt install conda -y
|
||||
source /opt/conda/etc/profile.d/conda.sh
|
||||
conda -V
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create Env:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
conda create -n dscb python=3.9
|
||||
conda activate dscb
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Install PROTOC
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
PROTOC_ZIP=protoc-21.12-linux-x86_64.zip
|
||||
curl -OL https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf/releases/download/v21.12/$PROTOC_ZIP
|
||||
@ -211,65 +36,29 @@ sudo unzip -o $PROTOC_ZIP -d /usr/local 'include/*'
|
||||
rm -f $PROTOC_ZIP
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
On MacOS, using Homebrew:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
brew install protobuf
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then run:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
BUILD_EXTENSIONS=True make install # Install repository and HF/transformer fork with CUDA kernels
|
||||
make run-falcon-7b-instruct
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** on some machines, you may also need the OpenSSL libraries and gcc. On Linux machines, run:
|
||||
|
||||
You might need to install these:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
sudo apt-get install libssl-dev gcc -y
|
||||
sudo apt-get install pkg-config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### CUDA Kernels
|
||||
|
||||
The custom CUDA kernels are only tested on NVIDIA A100s. If you have any installation or runtime issues, you can remove
|
||||
the kernels by using the `DISABLE_CUSTOM_KERNELS=True` environment variable.
|
||||
|
||||
Be aware that the official Docker image has them enabled by default.
|
||||
|
||||
## Run Falcon
|
||||
|
||||
### Run
|
||||
|
||||
Install DeepSparse:
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
make run-falcon-7b-instruct
|
||||
pip install deepsparse-nightly[transformers]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Quantization
|
||||
|
||||
You can also quantize the weights with bitsandbytes to reduce the VRAM requirement:
|
||||
|
||||
Install Server
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
make run-falcon-7b-instruct-quantize
|
||||
make install-server
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Develop
|
||||
|
||||
Launch Server
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
python3 server/text_generation_server/cli.py download-weights bigscience/bloom-560m
|
||||
python3 server/text_generation_server/cli.py serve bigscience/bloom-560m
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Launch Router
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
make server-dev
|
||||
make router-dev
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Testing
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
# python
|
||||
make python-server-tests
|
||||
make python-client-tests
|
||||
# or both server and client tests
|
||||
make python-tests
|
||||
# rust cargo tests
|
||||
make rust-tests
|
||||
# integration tests
|
||||
make integration-tests
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
2154
interaction.ipynb
Normal file
2154
interaction.ipynb
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
1274
server-dev.ipynb
Normal file
1274
server-dev.ipynb
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
251
server/deepsparse/deepsparse_causal_lm.py
Normal file
251
server/deepsparse/deepsparse_causal_lm.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,251 @@
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass
|
||||
from typing import List, Dict, Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, PreTrainedTokenizerBase
|
||||
|
||||
from server.deepsparse.deepsparse_model import (
|
||||
DeepSparsePastKeyValues, DeepSparseDecoderModel
|
||||
)
|
||||
from server.deepsparse.deepsparse_requests import (
|
||||
Request, Batch, CachedBatch, Generation
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
DEEPSPARSE_SEQUENCE_LENGTH = 128
|
||||
DEEPSPARSE_MULTITOKEN_LENGTH = 4
|
||||
|
||||
@dataclass
|
||||
class DeepSparseCausalLMBatch:
|
||||
batch_id: int
|
||||
requests: List[Request]
|
||||
requests_idx_mapping: Dict[int,int]
|
||||
input_ids_list: List[np.ndarray]
|
||||
past_key_values_list: List[Optional[DeepSparsePastKeyValues]]
|
||||
|
||||
@classmethod
|
||||
def from_batch(
|
||||
cls,
|
||||
batch: Batch,
|
||||
tokenizer: PreTrainedTokenizerBase,
|
||||
) -> "DeepSparseCausalLMBatch":
|
||||
|
||||
# parse batch
|
||||
requests_idx_mapping = {}
|
||||
input_ids_list = []
|
||||
|
||||
# setup tokenizer for deepsparse left padding
|
||||
tokenizer.padding_side = "left"
|
||||
if not tokenizer.pad_token:
|
||||
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token
|
||||
padding, truncation = "longest", False
|
||||
|
||||
# loop through items in the batch
|
||||
for idx, r in enumerate(batch.requests):
|
||||
requests_idx_mapping[r.id] = idx
|
||||
|
||||
# setup inputs_ids, past_key_values
|
||||
tokenized_inputs = tokenizer(
|
||||
r.prompt,
|
||||
return_tensors="np",
|
||||
padding=padding,
|
||||
truncation=truncation,
|
||||
return_token_type_ids=False,
|
||||
max_length=DEEPSPARSE_SEQUENCE_LENGTH
|
||||
)
|
||||
input_ids_list.append(tokenized_inputs["input_ids"])
|
||||
|
||||
return cls(
|
||||
batch_id=batch.id,
|
||||
requests=batch.requests,
|
||||
requests_idx_mapping=requests_idx_mapping,
|
||||
input_ids_list=input_ids_list,
|
||||
past_key_values_list=[None] * len(batch.requests),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def to_batch(self) -> CachedBatch:
|
||||
return CachedBatch(
|
||||
batch_id = self.batch_id,
|
||||
request_ids=[r.id for r in self.requests],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# length of the batch
|
||||
def __len__(self):
|
||||
return len(self.requests)
|
||||
|
||||
# pass list of request ids, returns batch with only those request ids
|
||||
def filter(self, request_ids: List[int]) -> Optional["DeepSparseCausalLMBatch"]:
|
||||
assert(len(request_ids) > 0)
|
||||
|
||||
requests_idx_mapping = {}
|
||||
requests = []
|
||||
input_ids_list = []
|
||||
past_key_values_list = []
|
||||
|
||||
# loop through requests, keep ones that should remain
|
||||
for new_idx, request_id in enumerate(request_ids):
|
||||
assert request_id in self.requests_idx_mapping.keys(), "all request ids must be in the batch"
|
||||
|
||||
requests_idx_mapping[request_id] = new_idx
|
||||
|
||||
old_idx = self.requests_idx_mapping[request_id]
|
||||
requests.append(self.requests[old_idx])
|
||||
input_ids_list.append(self.input_ids_list[old_idx])
|
||||
past_key_values_list.append(self.past_key_values_list[old_idx])
|
||||
|
||||
# update batch state
|
||||
self.requests = requests
|
||||
self.requests_idx_mapping = requests_idx_mapping
|
||||
self.input_ids_list = input_ids_list
|
||||
self.past_key_values_list = past_key_values_list
|
||||
|
||||
return self
|
||||
|
||||
# combine two batches into one
|
||||
@classmethod
|
||||
def concatenate(cls, batches: List["DeepSparseCausalLMBatch"]) -> "DeepSparseCausalLMBatch":
|
||||
assert len(batches) > 1, "must have more than 1 batch to concatenate"
|
||||
|
||||
requests_idx_mapping = {}
|
||||
requests = []
|
||||
input_ids_list = []
|
||||
past_key_values_list = []
|
||||
|
||||
start_index = 0
|
||||
for i, batch in enumerate(batches):
|
||||
assert batch.past_key_values_list is not None, "only concatenate prefilled batches"
|
||||
|
||||
# concatenate request, input_ids, and past_key_values lists
|
||||
requests.extend(batch.requests)
|
||||
input_ids_list.extend(batch.input_ids_list)
|
||||
past_key_values_list.extend(batch.past_key_values_list)
|
||||
|
||||
# merge the request_id to index mapping
|
||||
if i == 0:
|
||||
requests_idx_mapping = batch.requests_idx_mapping
|
||||
else:
|
||||
for k, v in batch.requests_idx_mapping.items():
|
||||
requests_idx_mapping[k] = v + start_index
|
||||
|
||||
start_index += len(batch)
|
||||
|
||||
return cls(
|
||||
batch_id=batches[0].batch_id,
|
||||
requests=requests,
|
||||
requests_idx_mapping=requests_idx_mapping,
|
||||
input_ids_list=input_ids_list,
|
||||
past_key_values_list=past_key_values_list
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
class DeepSparseCausalLM:
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
model_path: str,
|
||||
tokenizer_path: str,
|
||||
):
|
||||
# setup tokenizer
|
||||
self.tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(tokenizer_path)
|
||||
self.tokenizer.padding_side = "left"
|
||||
if not self.tokenizer.pad_token:
|
||||
assert self.tokenizer.eos_token
|
||||
self.tokenizer.pad_token = self.tokenizer.eos_token
|
||||
|
||||
# setup model
|
||||
self.model = DeepSparseDecoderModel(
|
||||
onnx_file_path = model_path,
|
||||
sequence_length = DEEPSPARSE_SEQUENCE_LENGTH,
|
||||
multitoken_length = DEEPSPARSE_MULTITOKEN_LENGTH,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# TODO (@rsnm2): switch to NextTokenChooser
|
||||
def sample_token(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
logits: np.ndarray
|
||||
):
|
||||
assert(logits.shape[0] == 1) # assert b=1 for now
|
||||
return np.argmax(logits[0,-1,:]) # grab logits for the last item in the sequence
|
||||
|
||||
# TODO (@rsnm2): switch to StoppingCriteria
|
||||
def should_stop(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
num_tokens_processed: int,
|
||||
generated_token_id: int
|
||||
):
|
||||
if num_tokens_processed >= self.model.sequence_length:
|
||||
return True
|
||||
if generated_token_id == self.tokenizer.eos_token_id:
|
||||
return True
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
def generate_token(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
batch: DeepSparseCausalLMBatch,
|
||||
) -> (List[Generation], Optional[DeepSparseCausalLMBatch]):
|
||||
|
||||
generations: List[Generation] = []
|
||||
all_stopped = True
|
||||
|
||||
# if we supported continuous batching, we would do batched inference here
|
||||
# logits, past_key_values = self.model(batch)
|
||||
|
||||
# for each member of the batch:
|
||||
# a) run inference
|
||||
# b) sample and check stopping criteria
|
||||
# c) create generation + update batch
|
||||
for i, (
|
||||
request,
|
||||
input_ids,
|
||||
past_key_values,
|
||||
) in enumerate(zip(
|
||||
batch.requests,
|
||||
batch.input_ids_list,
|
||||
batch.past_key_values_list
|
||||
)):
|
||||
|
||||
# run inference
|
||||
logits, past_key_values = self.model(input_ids, past_key_values)
|
||||
|
||||
# sample token
|
||||
# todo: simple for now --- should use NextTokenChooser
|
||||
generated_token_id = self.sample_token(logits)
|
||||
|
||||
# check stopping criteria
|
||||
# todo: simple for now --- should use StoppingCriteria
|
||||
assert len(input_ids.shape) == 2
|
||||
assert input_ids.shape[0] == 1
|
||||
|
||||
stop = self.should_stop(
|
||||
num_tokens_processed=input_ids.shape[1] + 1,
|
||||
generated_token_id = generated_token_id
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# if not stopped, convert token id to text
|
||||
generated_text = None
|
||||
if not stop:
|
||||
all_stopped = False
|
||||
generated_text = self.tokenizer.decode(
|
||||
generated_token_id,
|
||||
skip_special_tokens=True,
|
||||
clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False
|
||||
)
|
||||
generations.append(Generation(
|
||||
request_id=request.id,
|
||||
generated_text=generated_text
|
||||
))
|
||||
|
||||
# update values in the batch
|
||||
# bad --- this does not occur in place
|
||||
assert len(batch.input_ids_list[i].shape) == 2
|
||||
assert batch.input_ids_list[i].shape[0] == 1
|
||||
batch.input_ids_list[i] = np.append(
|
||||
batch.input_ids_list[i],
|
||||
np.array([[generated_token_id]]),
|
||||
axis=1
|
||||
)
|
||||
batch.past_key_values_list[i] = past_key_values
|
||||
|
||||
# if all elements of the batch are done, return generation + null for batch
|
||||
if all_stopped:
|
||||
return generations, None
|
||||
|
||||
# return generation + updated batch
|
||||
return generations, batch
|
||||
241
server/deepsparse/deepsparse_model.py
Normal file
241
server/deepsparse/deepsparse_model.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,241 @@
|
||||
import os
|
||||
os.environ["WAND_OPT_FLAGS"] = "default,~pyramids"
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from typing import Optional, List, Dict
|
||||
|
||||
from deepsparse import Context
|
||||
from deepsparse.engine import LIB
|
||||
from deepsparse.pipeline import DEEPSPARSE_ENGINE, create_engine
|
||||
from deepsparse.transformers.utils.helpers import overwrite_onnx_model_inputs, create_causal_mask
|
||||
|
||||
PAST_KEY_VALUES_NAME = "past_key_values"
|
||||
|
||||
class DeepSparsePastKeyValues:
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
prev_num_tokens = 0
|
||||
num_frozen_tokens = 1
|
||||
self.internal_past_key_values = LIB.kv_cache(prev_num_tokens, num_frozen_tokens)
|
||||
|
||||
class DeepSparseDecoderEngine:
|
||||
def __init__ (
|
||||
self,
|
||||
onnx_file_path: str,
|
||||
sequence_length: int = 1024,
|
||||
input_ids_length: int = 1,
|
||||
engine_context: Optional[Context] = None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
|
||||
# setup ONNX graph
|
||||
onnx_file_path, cached_outputs, data_type = overwrite_onnx_model_inputs(
|
||||
onnx_file_path=onnx_file_path,
|
||||
batch_size=1,
|
||||
sequence_length=sequence_length,
|
||||
input_ids_length=input_ids_length,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# compile engine
|
||||
self.engine = create_engine(
|
||||
onnx_file_path=onnx_file_path,
|
||||
engine_type=DEEPSPARSE_ENGINE,
|
||||
engine_args={"cached_outputs": cached_outputs},
|
||||
context=engine_context,
|
||||
)
|
||||
print(self.engine)
|
||||
|
||||
# save utilties
|
||||
self.past_key_value_dtype = data_type
|
||||
self.onnx_inputs = self.engine.input_names
|
||||
self.empty_past_key_values = self.make_empty_past_key_values()
|
||||
|
||||
# forward function
|
||||
def __call__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
engine_inputs: Dict[str, np.ndarray],
|
||||
past_key_values: DeepSparsePastKeyValues,
|
||||
val_inputs: bool = True
|
||||
):
|
||||
# format input into lists (we pass empty past key values)
|
||||
inputs = [
|
||||
self.empty_past_key_values[name] if name.startswith(PAST_KEY_VALUES_NAME)
|
||||
else engine_inputs[name] for name in self.engine.input_names
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
# validate inputs formatted correctly
|
||||
if val_inputs:
|
||||
self.engine._validate_inputs(inputs)
|
||||
|
||||
# run inference, updates past_key_values internally
|
||||
output = self.engine._eng_net.execute_list_out(
|
||||
inputs,
|
||||
past_key_values.internal_past_key_values
|
||||
)
|
||||
logits = output[0]
|
||||
return logits, past_key_values
|
||||
|
||||
# empty past kvs (dummy values to be passed around)
|
||||
def make_empty_past_key_values(self):
|
||||
past_key_values = {}
|
||||
for idx, name in enumerate(self.onnx_inputs):
|
||||
if name.startswith(PAST_KEY_VALUES_NAME):
|
||||
past_key_values[name] = np.zeros(
|
||||
self.engine.input_shapes[idx],
|
||||
dtype=self.past_key_value_dtype
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return past_key_values
|
||||
|
||||
class DeepSparseDecoderModel:
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
onnx_file_path: str,
|
||||
sequence_length: int = 1024,
|
||||
multitoken_length: int = 16,
|
||||
engine_context: Optional[Context] = None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
self.sequence_length = sequence_length
|
||||
self.multitoken_length = multitoken_length
|
||||
|
||||
# compile decode engine
|
||||
self.singletoken_engine = DeepSparseDecoderEngine(
|
||||
onnx_file_path=onnx_file_path,
|
||||
engine_context=engine_context,
|
||||
sequence_length=sequence_length,
|
||||
input_ids_length=1,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# compile prefill engine
|
||||
self.multitoken_engine = DeepSparseDecoderEngine(
|
||||
onnx_file_path=onnx_file_path,
|
||||
engine_context=engine_context,
|
||||
sequence_length=sequence_length,
|
||||
input_ids_length=self.multitoken_length,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert "input_ids" in self.singletoken_engine.onnx_inputs
|
||||
assert "attention_mask" in self.singletoken_engine.onnx_inputs
|
||||
assert "causal_mask" in self.singletoken_engine.onnx_inputs
|
||||
assert "positions" in self.singletoken_engine.onnx_inputs
|
||||
|
||||
def engine_inputs_for_prefill(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
input_ids: np.ndarray,
|
||||
):
|
||||
# split batch into N token_batches
|
||||
num_batches = input_ids.shape[1] // self.multitoken_length
|
||||
token_batches = [
|
||||
input_ids[:, i*self.multitoken_length : (i+1)*self.multitoken_length]
|
||||
for i in range(0, num_batches)
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
# format inputs for each of the N token_batches
|
||||
for idx, token_batch in enumerate(token_batches):
|
||||
num_processed_tokens = self.multitoken_length * idx
|
||||
|
||||
engine_inputs = {}
|
||||
engine_inputs["input_ids"] = token_batch
|
||||
|
||||
# make attention mask from the right
|
||||
engine_inputs["attention_mask"] = np.zeros((1, self.sequence_length), dtype=np.int64)
|
||||
engine_inputs["attention_mask"][:, -(self.multitoken_length + num_processed_tokens):] = 1
|
||||
|
||||
# make positions (building from the right)
|
||||
# TODO: handle case when multitoken engine is 1
|
||||
assert self.multitoken_length > 1
|
||||
engine_inputs["positions"] = np.arange(
|
||||
num_processed_tokens, num_processed_tokens + self.multitoken_length
|
||||
).reshape(1, -1).astype(np.int64)
|
||||
|
||||
# make causal mask (building from the right)
|
||||
engine_inputs["causal_mask"] = create_causal_mask(
|
||||
input_ids=engine_inputs["input_ids"],
|
||||
attention_mask=engine_inputs["attention_mask"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
yield engine_inputs
|
||||
|
||||
def engine_inputs_for_decode(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
input_ids: np.ndarray,
|
||||
):
|
||||
engine_inputs = {}
|
||||
engine_inputs["input_ids"] = input_ids[:,-1:]
|
||||
engine_inputs["attention_mask"] = np.zeros((1, self.sequence_length), dtype=np.int64)
|
||||
engine_inputs["attention_mask"][:, -input_ids.shape[1]:] = 1
|
||||
|
||||
engine_inputs["causal_mask"] = create_causal_mask(
|
||||
engine_inputs["input_ids"],
|
||||
engine_inputs["attention_mask"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
engine_inputs["positions"] = np.array([[input_ids.shape[1] - 1]], dtype=np.int64)
|
||||
|
||||
return engine_inputs
|
||||
|
||||
def decode(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
input_ids: np.ndarray,
|
||||
past_key_values: DeepSparsePastKeyValues
|
||||
) -> (np.ndarray, DeepSparsePastKeyValues):
|
||||
|
||||
# assert input is of shape [1,seq_len] w/ seq_len < self.sequence_len
|
||||
assert len(input_ids.shape) == 2
|
||||
assert input_ids.shape[0] == 1
|
||||
assert input_ids.shape[1] < self.sequence_length
|
||||
|
||||
engine_inputs = self.engine_inputs_for_decode(input_ids)
|
||||
logits, past_key_values = self.singletoken_engine(
|
||||
engine_inputs,
|
||||
past_key_values
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return logits, past_key_values
|
||||
|
||||
def prefill(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
input_ids: np.ndarray,
|
||||
) -> (np.ndarray, DeepSparsePastKeyValues):
|
||||
|
||||
# assert input is of shape [1,seq_len] w/ seq_len < self.sequence_len
|
||||
assert len(input_ids.shape) == 2
|
||||
assert input_ids.shape[0] == 1
|
||||
assert input_ids.shape[1] < self.sequence_length
|
||||
|
||||
tokens_processed = 0
|
||||
|
||||
# setup empty past key values
|
||||
past_key_values = DeepSparsePastKeyValues()
|
||||
|
||||
# loop through chunks, run inference w/ multitoken engine
|
||||
for engine_inputs in self.engine_inputs_for_prefill(input_ids):
|
||||
logits, past_key_values = self.multitoken_engine(
|
||||
engine_inputs,
|
||||
past_key_values
|
||||
)
|
||||
tokens_processed += self.multitoken_length
|
||||
|
||||
# if anything left over, run inference w/ singletoken engine
|
||||
while tokens_processed < input_ids.shape[1]:
|
||||
logits, past_key_values = self.decode(
|
||||
input_ids=input_ids[:,:tokens_processed+1],
|
||||
past_key_values=past_key_values
|
||||
)
|
||||
tokens_processed += 1
|
||||
# print(logits[:,-1:,:])
|
||||
|
||||
return logits, past_key_values
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
input_ids: np.ndarray,
|
||||
past_key_values: Optional[DeepSparsePastKeyValues] = None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
if past_key_values is None:
|
||||
return self.prefill(input_ids)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return self.decode(input_ids, past_key_values)
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
input_ids: np.ndarray,
|
||||
past_key_values: Optional[DeepSparsePastKeyValues] = None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
return self.forward(input_ids, past_key_values)
|
||||
58
server/deepsparse/deepsparse_queue.py
Normal file
58
server/deepsparse/deepsparse_queue.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
from typing import Deque, Optional, Tuple, Dict
|
||||
from collections import deque
|
||||
from threading import Condition
|
||||
from server.deepsparse.deepsparse_requests import Batch, Request
|
||||
|
||||
class GenerateRequest:
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
prompt: str,
|
||||
max_generated_tokens: int
|
||||
):
|
||||
self.prompt = prompt
|
||||
self.generation = prompt
|
||||
self.max_generated_tokens = max_generated_tokens
|
||||
self.cv = Condition()
|
||||
self.is_stopped = False
|
||||
|
||||
# todo: implement logic for maximum memory usage
|
||||
class DeepSparseQueue:
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
self.next_request_id: int = 0
|
||||
self.next_batch_id: int = 0
|
||||
self.queue: Deque[GenerateRequest] = deque()
|
||||
|
||||
def append(self, generate_request: GenerateRequest):
|
||||
self.queue.append(generate_request)
|
||||
|
||||
def is_empty(self):
|
||||
return len(self.queue) == 0
|
||||
|
||||
# (todo): enable multiple prefill requests in a batch
|
||||
def next_batch(self) -> Optional[Tuple[Batch, Dict[int, GenerateRequest]]]:
|
||||
if self.is_empty():
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
# pop first generate_request in the queue
|
||||
generate_request = self.queue.popleft()
|
||||
generate_requests = {
|
||||
self.next_request_id: generate_request
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# format into request
|
||||
request = Request(
|
||||
id=self.next_request_id,
|
||||
prompt=generate_request.prompt,
|
||||
max_generated_tokens=generate_request.max_generated_tokens
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.next_request_id += 1
|
||||
|
||||
# format into batch
|
||||
batch = Batch(
|
||||
id = self.next_batch_id,
|
||||
requests=[request]
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.next_batch_id += 1
|
||||
|
||||
# return batch, generate_requests
|
||||
return (batch, generate_requests)
|
||||
39
server/deepsparse/deepsparse_requests.py
Normal file
39
server/deepsparse/deepsparse_requests.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass
|
||||
from typing import List, Optional
|
||||
|
||||
@dataclass
|
||||
class Request:
|
||||
id: int
|
||||
prompt: str
|
||||
max_generated_tokens: int
|
||||
|
||||
@dataclass
|
||||
class Batch:
|
||||
id: int
|
||||
requests: List[Request]
|
||||
|
||||
@dataclass
|
||||
class CachedBatch:
|
||||
batch_id: int
|
||||
request_ids: List[int]
|
||||
|
||||
def __len__(self):
|
||||
return len(self.request_ids)
|
||||
|
||||
@dataclass
|
||||
class Generation:
|
||||
request_id: int
|
||||
generated_text: Optional[str]
|
||||
|
||||
@dataclass
|
||||
class PrefillRequest:
|
||||
batch: Batch
|
||||
|
||||
@dataclass
|
||||
class DecodeRequest:
|
||||
batches: List[CachedBatch]
|
||||
|
||||
@dataclass
|
||||
class FilterBatchRequest:
|
||||
batch_id: int
|
||||
request_ids: List[int]
|
||||
184
server/deepsparse/deepsparse_router.py
Normal file
184
server/deepsparse/deepsparse_router.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,184 @@
|
||||
from threading import Condition
|
||||
from typing import List, Dict, Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from server.deepsparse.deepsparse_service import DeepSparseService
|
||||
from server.deepsparse.deepsparse_requests import (
|
||||
CachedBatch, Batch, Generation,
|
||||
PrefillRequest, DecodeRequest, FilterBatchRequest,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from server.deepsparse.deepsparse_queue import (
|
||||
DeepSparseQueue, GenerateRequest
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
class DeepSparseRouter:
|
||||
def __init__(self, service: DeepSparseService):
|
||||
self.service: DeepSparseService = service
|
||||
self.queue: DeepSparseQueue = DeepSparseQueue()
|
||||
self.cv: Condition = Condition()
|
||||
|
||||
def generate(self, prompt:str) -> str:
|
||||
generate_request = GenerateRequest(
|
||||
prompt=prompt,
|
||||
max_generated_tokens=100
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
with self.cv:
|
||||
# print("router: acquired cv")
|
||||
self.queue.append(generate_request)
|
||||
self.cv.notify()
|
||||
|
||||
if prompt == "stop":
|
||||
return "stop"
|
||||
|
||||
with generate_request.cv:
|
||||
# print("generate_request: acquired cv")
|
||||
if not generate_request.is_stopped:
|
||||
# print("generate_request: waiting")
|
||||
generate_request.cv.wait()
|
||||
|
||||
# print("generate_request: done waiting")
|
||||
|
||||
return generate_request.generation
|
||||
|
||||
def prefill(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
batch: Batch,
|
||||
generate_requests: Dict[int,GenerateRequest]
|
||||
) -> Optional[CachedBatch]:
|
||||
# print("prefill")
|
||||
generation, next_batch = self.service.Prefill(
|
||||
PrefillRequest(batch=batch)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
self.filter_notify_update([generation], generate_requests)
|
||||
|
||||
return self.filter_batch(
|
||||
batch=next_batch,
|
||||
generate_requests=generate_requests
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def decode(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
batches: List[CachedBatch],
|
||||
generate_requests: Dict[int,GenerateRequest]
|
||||
) -> Optional[CachedBatch]:
|
||||
# print("decode")
|
||||
generations, next_batch = self.service.Decode(
|
||||
DecodeRequest(batches=batches)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
self.filter_notify_update(generations, generate_requests)
|
||||
|
||||
return self.filter_batch(
|
||||
batch=next_batch,
|
||||
generate_requests=generate_requests
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def filter_notify_update(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
generations: List[Generation],
|
||||
generate_requests: Dict[int, GenerateRequest]
|
||||
):
|
||||
# print("filter_notify_update")
|
||||
for generation in generations:
|
||||
request_id = generation.request_id
|
||||
|
||||
# if we hit a stopping criteria
|
||||
if generation.generated_text is None:
|
||||
# remove from active requests and notify
|
||||
stopped_generate_request = generate_requests.pop(request_id)
|
||||
with stopped_generate_request.cv:
|
||||
stopped_generate_request.is_stopped = True
|
||||
stopped_generate_request.cv.notify()
|
||||
|
||||
# otherwise, update generation
|
||||
else:
|
||||
generate_requests[request_id].generation += generation.generated_text
|
||||
|
||||
def filter_batch(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
batch: Optional[CachedBatch],
|
||||
generate_requests: Dict[int, GenerateRequest]
|
||||
) -> Optional[CachedBatch]:
|
||||
# print("filter_batch")
|
||||
|
||||
# batch is already done
|
||||
if batch is None:
|
||||
return batch
|
||||
|
||||
# no need to filter
|
||||
if len(batch) == len(generate_requests):
|
||||
return batch
|
||||
|
||||
# retain only requests that are still in active generation requests
|
||||
batch.request_ids = [id for id in batch.request_ids if id in generate_requests]
|
||||
|
||||
# if all requests complete, clear cache and return None
|
||||
if len(batch) == 0:
|
||||
self.service.ClearCache()
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
# otherwise call the filter batch service
|
||||
return self.service.FilterBatch(
|
||||
FilterBatchRequest(
|
||||
batch_id=batch.batch_id,
|
||||
request_ids=batch.request_ids,
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def batching_task(
|
||||
router: DeepSparseRouter
|
||||
) -> bool:
|
||||
# infinite_loop
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
# block while the queue is empty
|
||||
# print("batching_task: about to acquire cv")
|
||||
with router.cv:
|
||||
while router.queue.is_empty():
|
||||
# print(f"batching_task cv: waiting")
|
||||
router.cv.wait()
|
||||
# print(f"batching_task: done waiting")
|
||||
|
||||
# loop until all batches in the queue are processed
|
||||
next_batch = router.queue.next_batch()
|
||||
while next_batch is not None:
|
||||
batch, generate_requests = next_batch
|
||||
|
||||
# hack to break out of the cycle
|
||||
if batch.requests[0].prompt == "stop":
|
||||
assert router.queue.is_empty()
|
||||
assert len(router.service.cache) == 0
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
cached_batch = router.prefill(
|
||||
batch=batch,
|
||||
generate_requests=generate_requests
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# loop until we do not reiceve any cached batch from the service (== until
|
||||
# all requests have met their stopping criteria
|
||||
while cached_batch is not None:
|
||||
# print(f"batch_size = {len(cached_batch)}")
|
||||
batches = [cached_batch]
|
||||
|
||||
# try to get a new batch and run prefill on this batch
|
||||
next_batch = router.queue.next_batch()
|
||||
if next_batch is not None:
|
||||
new_batch, new_generate_requests = next_batch
|
||||
new_cached_batch = router.prefill(
|
||||
batch=new_batch,
|
||||
generate_requests=new_generate_requests
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if new_cached_batch is not None:
|
||||
batches.append(new_cached_batch)
|
||||
assert len(generate_requests.keys() & new_generate_requests.keys()) == 0
|
||||
generate_requests.update(new_generate_requests)
|
||||
|
||||
# run decode
|
||||
cached_batch = router.decode(
|
||||
batches=batches,
|
||||
generate_requests=generate_requests
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
next_batch = router.queue.next_batch()
|
||||
93
server/deepsparse/deepsparse_service.py
Normal file
93
server/deepsparse/deepsparse_service.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
|
||||
from typing import Optional, Dict, List
|
||||
from server.deepsparse.deepsparse_causal_lm import (
|
||||
DeepSparseCausalLM, DeepSparseCausalLMBatch
|
||||
)
|
||||
from server.deepsparse.deepsparse_requests import (
|
||||
PrefillRequest, DecodeRequest, FilterBatchRequest,
|
||||
Generation, CachedBatch
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
class Cache:
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
self.cache: Dict[int, DeepSparseCausalLMBatch] = {}
|
||||
|
||||
def pop(self, batch_id: int) -> Optional[DeepSparseCausalLMBatch]:
|
||||
return self.cache.pop(batch_id, None)
|
||||
|
||||
def set(self, entry: DeepSparseCausalLMBatch):
|
||||
if entry is not None:
|
||||
self.cache[entry.batch_id] = entry
|
||||
|
||||
def delete(self, batch_id: int):
|
||||
batch = self.pop(batch_id)
|
||||
if batch is not None:
|
||||
del batch
|
||||
|
||||
def clear(self):
|
||||
keys = list(self.cache.keys())
|
||||
for k in keys:
|
||||
self.delete(k)
|
||||
|
||||
def __len__(self):
|
||||
return len(self.cache.keys())
|
||||
|
||||
class DeepSparseService:
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
model: DeepSparseCausalLM
|
||||
):
|
||||
self.model = model
|
||||
self.cache = Cache()
|
||||
|
||||
def ClearCache(self):
|
||||
self.cache.clear()
|
||||
|
||||
def FilterBatch(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
request: FilterBatchRequest
|
||||
) -> CachedBatch:
|
||||
|
||||
ds_batch = self.cache.pop(request.batch_id)
|
||||
assert ds_batch is not None, "Batch ID {request.batch_id} not found in cache."
|
||||
filtered_batch = ds_batch.filter(request.request_ids)
|
||||
self.cache.set(filtered_batch)
|
||||
|
||||
return filtered_batch.to_batch()
|
||||
|
||||
def Prefill(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
request: PrefillRequest
|
||||
) -> [Generation, CachedBatch]:
|
||||
|
||||
ds_batch = DeepSparseCausalLMBatch.from_batch(
|
||||
batch=request.batch,
|
||||
tokenizer=self.model.tokenizer
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
generations, next_ds_batch = self.model.generate_token(ds_batch)
|
||||
assert len(generations) == 1
|
||||
self.cache.set(next_ds_batch)
|
||||
|
||||
return generations[0], next_ds_batch.to_batch()
|
||||
|
||||
def Decode(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
request: DecodeRequest
|
||||
) -> [List[Generation], CachedBatch]:
|
||||
assert len(request.batches) != 0, "Must provide at least one batch"
|
||||
|
||||
ds_batches = []
|
||||
for batch in request.batches:
|
||||
ds_batch = self.cache.pop(batch.batch_id)
|
||||
assert batch is not None, "Batch ID {batch.id} not found in cache."
|
||||
ds_batches.append(ds_batch)
|
||||
|
||||
if len(ds_batches) > 1:
|
||||
ds_batch = DeepSparseCausalLMBatch.concatenate(ds_batches)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
ds_batch = ds_batches[0]
|
||||
|
||||
generations, next_ds_batch = self.model.generate_token(ds_batch)
|
||||
self.cache.set(next_ds_batch)
|
||||
|
||||
return generations, (next_ds_batch.to_batch() if next_ds_batch else None)
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user