13 KiB
Snapshot Checksum Calculation and Bit Rot Detection
Summary
Longhorn system supports volume snapshotting and stores the snapshot disk files on the local disk. However, it is impossible to check the data integrity of snapshots due to the lack of the checksums of the snapshots in current implementation. As a result, if the underlying storage bit rots, no way is available to detect the data corruption and repair the replicas. In the enhancement, the snapshot checksum is calculated after the snapshot is taken and is checked periodically. When a corrupted snapshot is detected, a replica rebuild is triggered to repair the snapshot.
Related Issues
- [IMPROVEMENT] Introduce checksum for snapshots
- [FEATURE] automatic identifying of corrupted replica (bit rot detection)
Motivation
Goals
- Automatic snapshot hashing
- Identify corrupted snapshot
- Trigger replica rebuild when a corrupted snapshot is detected
Non-goals
- The hashing/checking mechanism is applied to detached volumes
- Support concurrent snapshot hashing
- In current architecture, the instance-manager-r does not have a proxy, so the snapshot requests are directly sent to the replica processes’ sync-agent servers. Hence, the concurrent limit cannot achieved in the instance-manager-r internally.
- From the benchmarking result, the checksum calculation eats too much io resource and impacts the system performance a lot. We also don’t know if the longhorn disks on a same physical disk or not. If they are on the same physical disk and the concurrent limit is larger than 1, the other workloads will be impacted significantly, and there might be a disaster for the entire system.
Proposal
User Stories
Bit rot in storage is rare but real, and it can corrupt the data silently. Longhorn supports volume snapshotting and restoring a volume to a previous version. However, due to the lack of the checksums of the snapshots in current implementation, it is impossible to ensure the data integrity of the replicas/snapshots. Although, we provide a method (ref) to identify the corrupted snapshots/replicas, the process is tedious and time-consuming for users.
User Experience In Detail
- Users' operations will not be affected by snapshot hashing and checking.
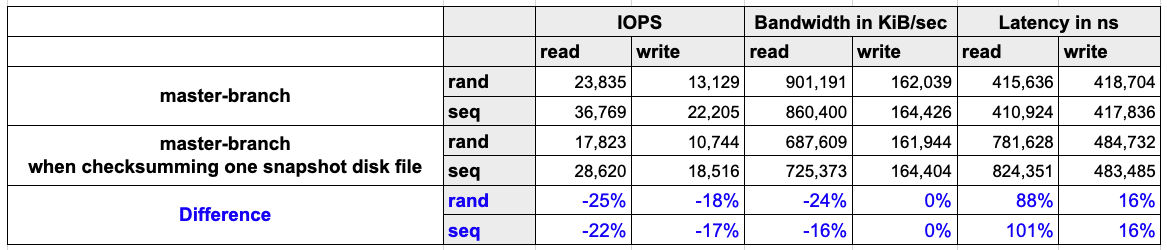
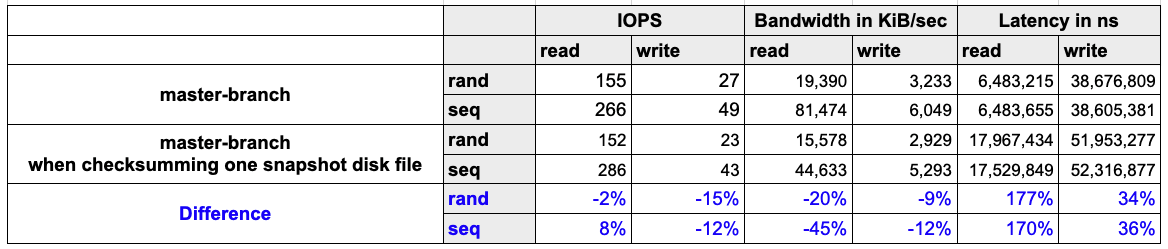
- The system will consume computing and disk IO resources while hashing snapshot disk files. In the meantime, the CPU usages are 380m and 900m when computing the CRC64 (ISO) and SHA256 values, respectively. In the implementation, the CRC64 (ISO) is utilized for detecting corruption.
-
The snapshot hashing benchmarking result is provided
-
The read performance will be impacted as well, as summarized in the below table.
- Environment
- Host: AWS EC2 c5d.2xlarge
- CPU: Intel(R) Xeon(R) Platinum 8124M CPU @ 3.00GHz
- Memory: 16 GB
- Network: Up to 10Gbps
- Kubernetes: v1.24.4+rke2r1
- Host: AWS EC2 c5d.2xlarge
- Result
- Environment
-
CLI
Add snapshot hash and snapshot hash-status commands
snaphost hashissues a snapshot hashing request to engine.- Usage:
longhorn --url ${engine-ip}:${engine-port} snapshot hash tcp://${replica-sync-agent-ip}:${replica-sync-agent-port} --snapshot-name ${name}
- Usage:
snapshot hash-statusrequests the snapshot hashing status from engine.- Usage:
longhorn --url ${engine-ip}:${engine-port} snapshot hash-status tcp://${replica-sync-agent-ip}:${replica-sync-agent-port}
- Usage:
snapshot hash-cancelcancels the snapshot hashing task.- Usage:
longhorn --url ${engine-ip}:${engine-port} snapshot hash-cancel tcp://${replica-sync-agent-ip}:${replica-sync-agent-port}
- Usage:
Engine Proxy gRPC API
Add SnapshotHash, SnapshotHashStatus and SnapshotHashCancel methods and their request and response messages.
SnapshotHashissues a snapshot hashing request to engine.SnapshotHashStatusrequests the snapshot hashing status from engine.SnapshotHashCancelcancels the snapshot hashing task.
Replica Sync-Agent gRPC API
Add SnapshotHash, SnapshotHashStatus and SnapshotHashCancel methods and their request and response messages.
SnapshotHashissues a snapshot hashing request to replica sync-agent.SnapshotHashStatusrequests the snapshot hashing status from replica sync-agent.SnapshotHashCancelcancels the snapshot hashing task.
Design
Implementation Overview
Global Settings
-
snapshot-data-integrity
- Description: A global setting for enabling or disabling snapshot data integrity checking mode.
- Type: string
- Value:
- disabled: Disable snapshot disk file hashing and data integrity checking.
- enabled: Enables periodic snapshot disk file hashing and data integrity checking. To detect the filesystem-unaware corruption caused by bit rot or other issues in snapshot disk files, Longhorn system periodically hashes files and finds corrupted ones. Hence, the system performance will be impacted during the periodical checking.
- fast-check: Enable snapshot disk file hashing and fast data integrity checking. Longhorn system only hashes snapshot disk files if they are not hashed or if the modification time changed. In this mode, filesystem-unaware corruption cannot be detected, but the impact on system performance can be minimized.
- Default:
disabled
-
snapshot-data-integrity-immediate-checking-after-snapshot-creation
- Description: Hashing snapshot disk files impacts the performance of the system. The immediate snapshot hashing and checking can be disabled to minimize the impact after creating a snapshot.
- Type: bool
- Default:
false
-
snapshot-data-integrity-cron-job
- Description: The setting is a set of five fields in a line, indicating when Longhorn checks the data integrity of snapshot disk files.
- Type: string (Cron job format)
- Default:
0 0 */7 * *(once a week)
CRDs
-
Volume
- Add
volume.spec.snapshotDataIntegrityfor setting the volume's snapshot data integrity checking mode. The value can beignored,disabled,enabledorfast-check.ignoredmeans the the volume's snapshot check is following the global settingsnapshot-data-integrity.- After upgrading Longhorn-system, the value is set to
ignoredfor an existing volumes whosevolume.spec.snapshotDataIntegrityis not set. - For a newly created volume, the value is
ignoredby default.
- Add
-
Snapshot
- Add
snapshot.status.checksumfor recording the snapshotcrc64(iso)checksum.
- Add
-
Node
- Add
node.status.snapshotPeriodicCheckStatus.statefor indicating current periodic check state. The value can beidleorin-progress. - Add
node.status.snapshotPeriodicCheckStatus.lastCheckedAtfor recording the start timestamp of the last checksum checking.
- Add
Automatic Snapshot Checksum Hashing and Checking
-
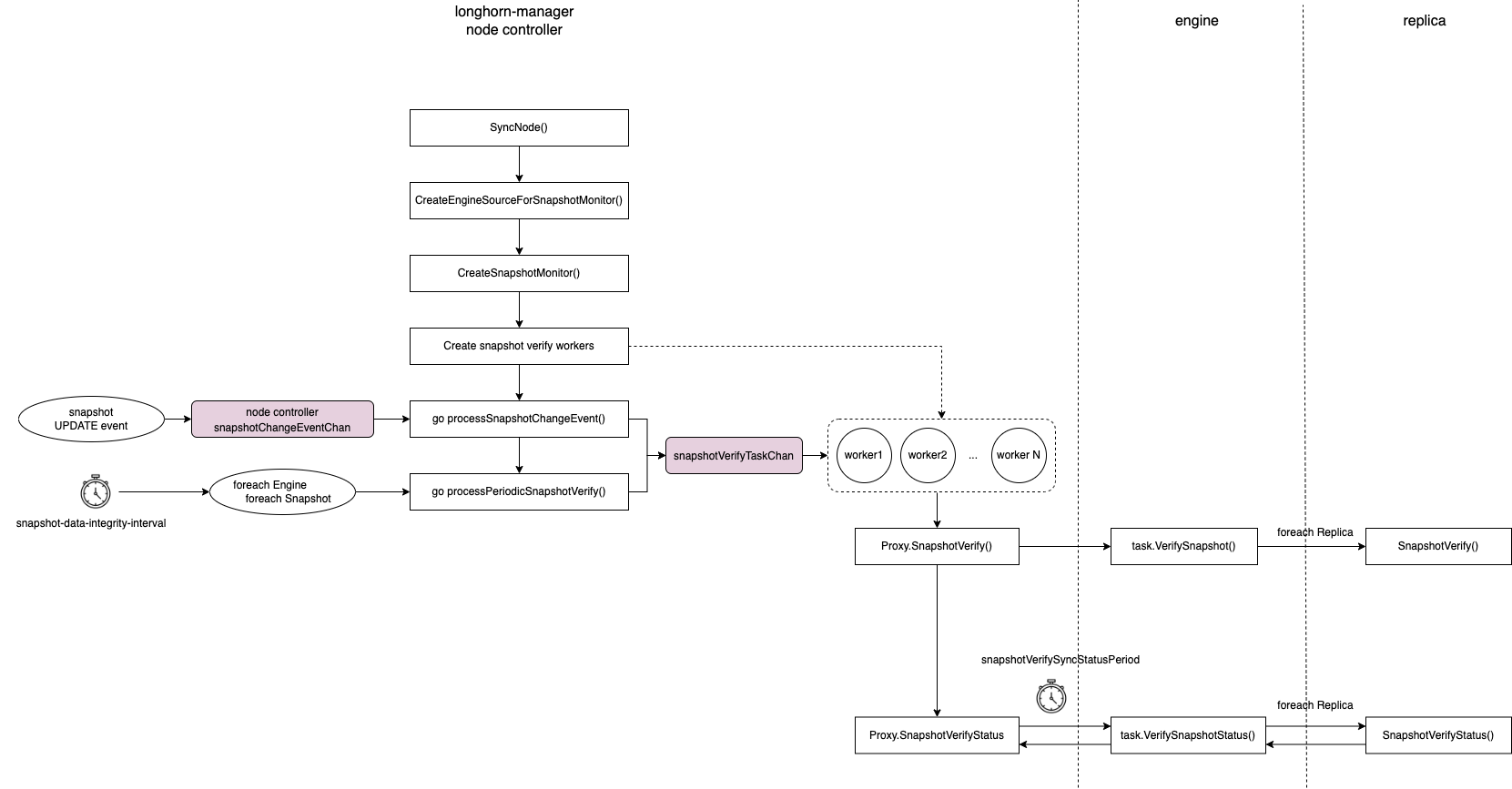
Node controller creates a snapshot monitor for hashing snapshot disk files as well as checking their data integrity. The monitor is consist of
-
1 goroutine
processSnapshotChangeEvent(): Send a snapshot hashing/checking task to thesnapshotCheckTaskQueueworkqueue after receiving one snapshotUPDATEevent. -
1 goroutine
processPeriodicSnapshotCheck(): Periodically create snapshot hashing/checking tasks. The period is determined by the global settingsnapshot-data-integrity-cron-job. When the job is started, it populates engines' snapshots and sends snapshot hashing/checking tasks to thesnapshotCheckTaskQueuechannel. -
N task workers: Issue hashing requests to engines and detect corrupted replicas according to the results.
-
-
Task workers fetch tasks from
snapshotCheckTaskQueueand check if the snapshot disk file needs to be hashed. The rules are -
Issue snapshot hashing requests to their associated engines. Then, the checksum of the snapshot disk file is calculated individually in the replica process. To ensure only one in-progress calculation, the worker holds the per-node file lock (
/host/var/lib/longhorn/.lock/hash) when calculating the checksum to avoid significant storage performance drop caused by the concurrent calculations. -
The worker waits until each snapshot disk file's checksum calculation has been completed. It periodically polls the engine and checks the status during the waiting period.
-
The worker gets the result once the calculation is completed. The result is like
map[string]string{ "pvc-abc-r-001": 0470c08fbc4dc702, "pvc-abc-r-002": 0470c08fbc4dc702, "pvc-abc-r-003": ce7c12a4d568fddf, } -
The final checksum is determined by the majority of the checksums with
SilentCorrupted=falsefrom replicas. For instance, the final checksum of the result in 4. is0470c08fbc4dc702.- When all checksums differ, the final checksum is unable to be determined
- If
snapshot.status.checksumis empty- Set all replicas to
ERR
- Set all replicas to
- If
snapshot.status.checksumis already set- Use the
snapshot.status.checksumas the final checksum, and set the replicas that have mismatching checksums toERR
- Use the
- If
- When the final checksum is successfully determined
- Assign the final checksum to
snapshot.status.checksum - Set the replica to
ERRif its snapshot disk file's checksum is not equal tosnapshot.status.checksum
- Assign the final checksum to
- If the final checksum cannot be determined, the event of the corruption detected is also emitted.
- For example, Longhorn will not do any error handling and just emits a event when the silent corruption is found in a single-replica volume.
- When all checksums differ, the final checksum is unable to be determined
-
Then, the replicas in
ERRmode will be rebuilt and fixed. The event of the corruption detected is also emitted.
Snapshot Disk File Hashing in Replica Process
When the replica process received the request of snapshot disk file hashing, the checking mode is determined by volume.spec.snapshotDataIntegrity. If the value is ignored, the checking mode follows the global setting snapshot-data-integrity.
-
fask-check- Flow
-
Get
ctimeinformation of the snapshot disk file. -
Get the value of the extended attribute
user.longhorn-system.metadatarecording the checksum andctimeof the file in the last calculation. The value ofuser.longhorn-system.metadatais JSON formatted string and recordshashing method,checksum,ctimeand etc. -
Compare the
ctimefrom 1. and 2. Recalculate the checksum if one of the conditions is met- The two
ctimeare mismatched. - 2's
ctimeis not existing.
- The two
-
Ensure that the checksum is reliable by getting the
ctimeinformation of the disk file again after the checksum calculation.- If it is matched with 1's
ctime, update the extended attribute with the latest result. - Instead, it indicates the file is changed by snapshot pruning, merging or other operations. Thus, recalculate the checksum. A maximum retries controls the recalculation.
- If it is matched with 1's
-
Return checksum or error to engine.
-
- Flow
-
enabled
- Because the silent data corruption in snapshot disk files can be caused by the host's storage device such as bit rot or somewhere within the storage stack. Filesystem cannot be aware of the corruption. To detect the corruption, the checksums of the disk files are always be recalculated and return back to engine. Silent corruption is detected when the disk file's
ctimematches thectimein the extended attribute, but the checksums do not match. The extended attribute will not be updated, and theSilentCorruptedof the hash status will be set totrue.
- Because the silent data corruption in snapshot disk files can be caused by the host's storage device such as bit rot or somewhere within the storage stack. Filesystem cannot be aware of the corruption. To detect the corruption, the checksums of the disk files are always be recalculated and return back to engine. Silent corruption is detected when the disk file's
-
disabled
- Do nothing.
Test Plan
Integration tests
- Test snapshot disk files hashing
- Compare the checksum recorded in
snapshot.status.checksumand the checksum (calculated by a 3rd-party CRC64 checksum utility of each replica's snapshot disk file.
- Compare the checksum recorded in
- Test snapshot disk files check
- Corrupt a snapshot disk file in one of the replicas. Then, check the corruption is detected by Longhorn, and the replica rebuilding should be triggered.
Note[optional]
3rd-party CRC64 Checksum Utility for Test Plan
- Install Java (
apt install default-jre default-jdk) - Download jacksum (
wget https://github.com/jonelo/jacksum/releases/download/v3.4.0/jacksum-3.4.0.jar) - Calculate checksum by
java -jar jacksum-3.4.0.jar -a crc64_go-iso ${path-to-file}