mirror of
https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference.git
synced 2025-09-10 20:04:52 +00:00
Merge branch 'main' into remove_readme
This commit is contained in:
commit
7c8f0a0546
@ -82,7 +82,6 @@ text-generation-launcher --help
|
||||
You can consult the OpenAPI documentation of the `text-generation-inference` REST API using the `/docs` route. The
|
||||
Swagger UI is also available at: [https://huggingface.github.io/text-generation-inference](https://huggingface.github.io/text-generation-inference).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### A note on Shared Memory (shm)
|
||||
|
||||
[`NCCL`](https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/nccl/user-guide/docs/index.html) is a communication framework used by
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ repository = "https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference"
|
||||
|
||||
[tool.poetry.dependencies]
|
||||
python = "^3.7"
|
||||
pydantic = "^1.10"
|
||||
pydantic = "> 1.10, < 3"
|
||||
aiohttp = "^3.8"
|
||||
huggingface-hub = ">= 0.12, < 1.0"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,7 +12,7 @@
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
__version__ = "0.3.0"
|
||||
__version__ = "0.6.0"
|
||||
|
||||
from text_generation.client import Client, AsyncClient
|
||||
from text_generation.inference_api import InferenceAPIClient, InferenceAPIAsyncClient
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,21 +18,21 @@ class Parameters(BaseModel):
|
||||
# Stop generating tokens if a member of `stop_sequences` is generated
|
||||
stop: List[str] = []
|
||||
# Random sampling seed
|
||||
seed: Optional[int]
|
||||
seed: Optional[int] = None
|
||||
# The value used to module the logits distribution.
|
||||
temperature: Optional[float]
|
||||
temperature: Optional[float] = None
|
||||
# The number of highest probability vocabulary tokens to keep for top-k-filtering.
|
||||
top_k: Optional[int]
|
||||
top_k: Optional[int] = None
|
||||
# If set to < 1, only the smallest set of most probable tokens with probabilities that add up to `top_p` or
|
||||
# higher are kept for generation.
|
||||
top_p: Optional[float]
|
||||
top_p: Optional[float] = None
|
||||
# truncate inputs tokens to the given size
|
||||
truncate: Optional[int]
|
||||
truncate: Optional[int] = None
|
||||
# Typical Decoding mass
|
||||
# See [Typical Decoding for Natural Language Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.00666) for more information
|
||||
typical_p: Optional[float]
|
||||
typical_p: Optional[float] = None
|
||||
# Generate best_of sequences and return the one if the highest token logprobs
|
||||
best_of: Optional[int]
|
||||
best_of: Optional[int] = None
|
||||
# Watermarking with [A Watermark for Large Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.10226)
|
||||
watermark: bool = False
|
||||
# Get generation details
|
||||
@ -114,7 +114,7 @@ class Request(BaseModel):
|
||||
# Prompt
|
||||
inputs: str
|
||||
# Generation parameters
|
||||
parameters: Optional[Parameters]
|
||||
parameters: Optional[Parameters] = None
|
||||
# Whether to stream output tokens
|
||||
stream: bool = False
|
||||
|
||||
@ -145,7 +145,7 @@ class InputToken(BaseModel):
|
||||
text: str
|
||||
# Logprob
|
||||
# Optional since the logprob of the first token cannot be computed
|
||||
logprob: Optional[float]
|
||||
logprob: Optional[float] = None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Generated tokens
|
||||
@ -180,7 +180,7 @@ class BestOfSequence(BaseModel):
|
||||
# Number of generated tokens
|
||||
generated_tokens: int
|
||||
# Sampling seed if sampling was activated
|
||||
seed: Optional[int]
|
||||
seed: Optional[int] = None
|
||||
# Decoder input tokens, empty if decoder_input_details is False
|
||||
prefill: List[InputToken]
|
||||
# Generated tokens
|
||||
@ -196,7 +196,7 @@ class Details(BaseModel):
|
||||
# Number of generated tokens
|
||||
generated_tokens: int
|
||||
# Sampling seed if sampling was activated
|
||||
seed: Optional[int]
|
||||
seed: Optional[int] = None
|
||||
# Decoder input tokens, empty if decoder_input_details is False
|
||||
prefill: List[InputToken]
|
||||
# Generated tokens
|
||||
@ -204,7 +204,7 @@ class Details(BaseModel):
|
||||
# Most likely tokens
|
||||
top_tokens: Optional[List[List[Token]]]
|
||||
# Additional sequences when using the `best_of` parameter
|
||||
best_of_sequences: Optional[List[BestOfSequence]]
|
||||
best_of_sequences: Optional[List[BestOfSequence]] = None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# `generate` return value
|
||||
@ -222,7 +222,7 @@ class StreamDetails(BaseModel):
|
||||
# Number of generated tokens
|
||||
generated_tokens: int
|
||||
# Sampling seed if sampling was activated
|
||||
seed: Optional[int]
|
||||
seed: Optional[int] = None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# `generate_stream` return value
|
||||
@ -233,10 +233,10 @@ class StreamResponse(BaseModel):
|
||||
top_tokens: Optional[List[Token]]
|
||||
# Complete generated text
|
||||
# Only available when the generation is finished
|
||||
generated_text: Optional[str]
|
||||
generated_text: Optional[str] = None
|
||||
# Generation details
|
||||
# Only available when the generation is finished
|
||||
details: Optional[StreamDetails]
|
||||
details: Optional[StreamDetails] = None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Inference API currently deployed model
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,7 +10,7 @@
|
||||
"name": "Apache 2.0",
|
||||
"url": "https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"version": "1.0.2"
|
||||
"version": "1.0.3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"paths": {
|
||||
"/": {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -21,4 +21,6 @@
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: conceptual/streaming
|
||||
title: Streaming
|
||||
- local: conceptual/flash_attention
|
||||
title: Flash Attention
|
||||
title: Conceptual Guides
|
||||
|
||||
12
docs/source/conceptual/flash_attention.md
Normal file
12
docs/source/conceptual/flash_attention.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
|
||||
# Flash Attention
|
||||
|
||||
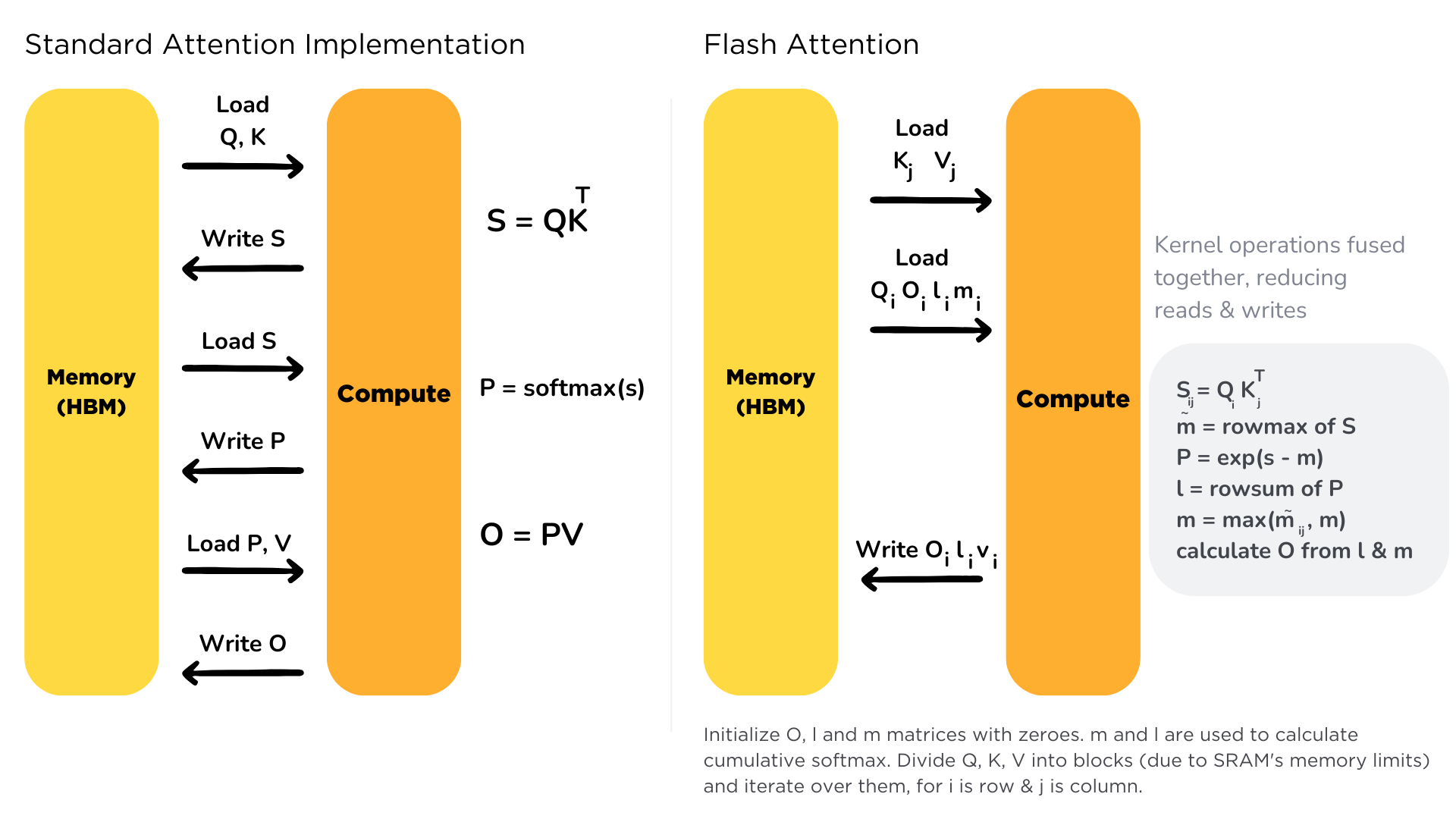
Scaling the transformer architecture is heavily bottlenecked by the self-attention mechanism, which has quadratic time and memory complexity. Recent developments in accelerator hardware mainly focus on enhancing compute capacities and not memory and transferring data between hardware. This results in attention operation having a memory bottleneck. **Flash Attention** is an attention algorithm used to reduce this problem and scale transformer-based models more efficiently, enabling faster training and inference.
|
||||
|
||||
Standard attention mechanism uses High Bandwidth Memory (HBM) to store, read and write keys, queries and values. HBM is large in memory, but slow in processing, meanwhile SRAM is smaller in memory, but faster in operations. In the standard attention implementation, the cost of loading and writing keys, queries, and values from HBM is high. It loads keys, queries, and values from HBM to GPU on-chip SRAM, performs a single step of the attention mechanism, writes it back to HBM, and repeats this for every single attention step. Instead, Flash Attention loads keys, queries, and values once, fuses the operations of the attention mechanism, and writes them back.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
It is implemented for supported models. You can check out the complete list of models that support Flash Attention [here](https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference/tree/main/server/text_generation_server/models), for models with flash prefix.
|
||||
|
||||
You can learn more about Flash Attention by reading the paper in this [link](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.14135).
|
||||
|
||||
@ -121,9 +121,9 @@ If you're using the free Inference API, you can use `HfInference`. If you're usi
|
||||
We can create a `HfInferenceEndpoint` providing our endpoint URL and credential.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import { HfInference } from '@huggingface/inference'
|
||||
import { HfInferenceEndpoint } from '@huggingface/inference'
|
||||
|
||||
const hf = new HfInference('https://YOUR_ENDPOINT.endpoints.huggingface.cloud', 'hf_YOUR_TOKEN')
|
||||
const hf = new HfInferenceEndpoint('https://YOUR_ENDPOINT.endpoints.huggingface.cloud', 'hf_YOUR_TOKEN')
|
||||
|
||||
// prompt
|
||||
const prompt = 'What can you do in Nuremberg, Germany? Give me 3 Tips'
|
||||
@ -143,6 +143,4 @@ SSEs are different than:
|
||||
* Polling: where the client keeps calling the server to get data. This means that the server might return empty responses and cause overhead.
|
||||
* Webhooks: where there is a bi-directional connection. The server can send information to the client, but the client can also send data to the server after the first request. Webhooks are more complex to operate as they don’t only use HTTP.
|
||||
|
||||
One of the limitations of Server-Sent Events is that they limit how many concurrent requests can handle by the server. Instead of timing out when there are too many SSE connections, TGI returns a HTTP Error with an `overloaded` error type (`huggingface_hub` returns `OverloadedError`). This allows the client to manage the overloaded server (e.g. it could display a busy error to the user or it could retry with a new request). To configure the maximum number of concurrent requests, you can specify `--max_concurrent_requests`, allowing to handle backpressure.
|
||||
|
||||
One of the limitations of Server-Sent Events is that they limit how many concurrent requests can handle by the server. Instead of timing out when there are too many SSE connections, TGI returns an HTTP Error with an `overloaded` error type (`huggingface_hub` returns `OverloadedError`). This allows the client to manage the overloaded server (e.g., it could display a busy error to the user or retry with a new request). To configure the maximum number of concurrent requests, you can specify `--max_concurrent_requests`, allowing clients to handle backpressure.
|
||||
If there are too many requests at the same time, TGI returns an HTTP Error with an `overloaded` error type (`huggingface_hub` returns `OverloadedError`). This allows the client to manage the overloaded server (e.g., it could display a busy error to the user or retry with a new request). To configure the maximum number of concurrent requests, you can specify `--max_concurrent_requests`, allowing clients to handle backpressure.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ Let's say you want to deploy [Falcon-7B Instruct](https://huggingface.co/tiiuae/
|
||||
model=tiiuae/falcon-7b-instruct
|
||||
volume=$PWD/data # share a volume with the Docker container to avoid downloading weights every run
|
||||
|
||||
docker run --gpus all --shm-size 1g -p 8080:80 -v $volume:/data ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:1.0.2 --model-id $model
|
||||
docker run --gpus all --shm-size 1g -p 8080:80 -v $volume:/data ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:1.0.3 --model-id $model
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
@ -85,7 +85,7 @@ curl 127.0.0.1:8080/generate \
|
||||
To see all possible deploy flags and options, you can use the `--help` flag. It's possible to configure the number of shards, quantization, generation parameters, and more.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
docker run ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:1.0.2 --help
|
||||
docker run ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:1.0.3 --help
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
vllm_commit := d284b831c17f42a8ea63369a06138325f73c4cf9
|
||||
vllm_commit := e86af624d059969b0fb07b075b1d338bf10c3365
|
||||
|
||||
vllm:
|
||||
# Clone vllm
|
||||
@ -10,4 +10,4 @@ build-vllm: vllm
|
||||
|
||||
install-vllm: build-vllm
|
||||
pip uninstall vllm -y || true
|
||||
cd vllm && python setup.py install
|
||||
cd vllm && python setup.py install
|
||||
|
||||
@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ class IdeficsVisionConfig(PretrainedConfig):
|
||||
Number of attention heads for each attention layer in the Transformer encoder.
|
||||
image_num_channels (`int`, *optional*, defaults to `3`):
|
||||
Number of image channels.
|
||||
hidden_act (`str` or `function`, *optional*, defaults to `"quick_gelu"`):
|
||||
hidden_act (`str` or `function`, *optional*, defaults to `"gelu"`):
|
||||
The non-linear activation function (function or string) in the encoder and pooler. If string, `"gelu"`,
|
||||
`"relu"`, `"selu"` and `"gelu_new"` ``"quick_gelu"` are supported.
|
||||
layer_norm_eps (`float`, *optional*, defaults to 1e-5):
|
||||
@ -80,7 +80,7 @@ class IdeficsVisionConfig(PretrainedConfig):
|
||||
num_hidden_layers=32,
|
||||
num_attention_heads=16,
|
||||
num_channels=3,
|
||||
hidden_act="quick_gelu",
|
||||
hidden_act="gelu",
|
||||
layer_norm_eps=1e-5,
|
||||
attention_dropout=0.0,
|
||||
initializer_range=0.02,
|
||||
|
||||
@ -54,7 +54,10 @@ class FlashRWSharded(FlashCausalLM):
|
||||
device,
|
||||
dtype,
|
||||
process_group=self.process_group,
|
||||
aliases={"lm_head.weight": ["transformer.word_embeddings.weight"]},
|
||||
aliases={
|
||||
"lm_head.weight": ["transformer.word_embeddings.weight"],
|
||||
"transformer.word_embeddings.weight": ["lm_head.weight"],
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
config.quantize = quantize
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,13 +18,20 @@ from accelerate import init_empty_weights
|
||||
|
||||
from text_generation_server.utils.gptq.quant_linear import QuantLinear
|
||||
|
||||
HAS_EXLLAMA = True
|
||||
try:
|
||||
major, _minor = torch.cuda.get_device_capability()
|
||||
except Exception:
|
||||
major = 1
|
||||
HAS_EXLLAMA = False
|
||||
CAN_EXLLAMA = major >= 8
|
||||
if os.getenv("DISABLE_EXLLAMA") == "True":
|
||||
HAS_EXLLAMA = False
|
||||
try:
|
||||
from text_generation_server.utils.gptq.exllama import Ex4bitLinear
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
HAS_EXLLAMA = False
|
||||
elif CAN_EXLLAMA:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
from text_generation_server.utils.gptq.exllama import Ex4bitLinear
|
||||
HAS_EXLLAMA = True
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -363,9 +363,10 @@ def batch_top_tokens(
|
||||
# Find the new "fuzzy" top n values
|
||||
top_n_indices = (logprobs >= nth_highest).nonzero()
|
||||
_, top_n_ishes = torch.unique_consecutive(top_n_indices[:, 0], return_counts=True)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
k = 1 if top_n_ishes.numel() == 0 else top_n_ishes.max()
|
||||
# Take a new topk for these new max n values
|
||||
top_k = torch.topk(logprobs, k=top_n_ishes.max(), dim=1, sorted=True)
|
||||
top_k = torch.topk(logprobs, k=k, dim=1, sorted=True)
|
||||
|
||||
top_n_ishes = top_n_ishes.tolist()
|
||||
top_indices = top_k.indices.tolist()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -170,10 +170,10 @@ class Weights:
|
||||
"Cannot load `gptq` weight, make sure the model is already quantized, or quantize it with `text-generation-server quantize ORIGINAL_MODEL_ID NEW_MODEL_ID`"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
from text_generation_server.utils.layers import HAS_EXLLAMA
|
||||
from text_generation_server.utils.layers import HAS_EXLLAMA, CAN_EXLLAMA
|
||||
|
||||
if use_exllama:
|
||||
if not HAS_EXLLAMA:
|
||||
if not HAS_EXLLAMA and CAN_EXLLAMA:
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
"Exllama GPTQ cuda kernels (which are faster) could have been used, but are not currently installed, try using BUILD_EXTENSIONS=True"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user